Is the Ebola Outbreak in DR Congo Claiming More Lives?
Published: 2025-09-04 15:54:04 | Category: world
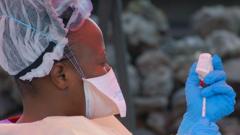
The recent outbreak of the Ebola virus in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has resulted in at least 15 fatalities, marking a significant public health crisis in a region already grappling with ongoing conflicts and inadequate healthcare infrastructure. The outbreak was confirmed following the hospitalisation of a pregnant woman displaying typical symptoms. The health ministry has reported 28 suspected cases, prompting urgent calls for preventive measures to mitigate further transmission.
Last updated: 24 October 2023 (BST)
Key Takeaways
- At least 15 people have died from the latest Ebola outbreak in DRC.
- The outbreak is concentrated in the central Kasai province with 28 suspected cases.
- The Zaire strain of Ebola virus has been confirmed.
- Health officials are urging strict preventive measures to stop the virus's spread.
- This marks the 16th outbreak of Ebola in the DRC since it was first detected in 1976.
Overview of the Current Outbreak
The latest Ebola outbreak in the DRC began with the confirmation of the virus in a 34-year-old pregnant woman who displayed symptoms such as high fever and vomiting. This case led to a series of investigations, which revealed multiple other suspected cases in the region. The health ministry's rapid response is vital given the virus's high fatality rate and the potential for widespread transmission.
Understanding Ebola Virus Disease
Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a serious and often deadly illness caused by the Ebola viruses, which are part of the Filoviridae family. The Zaire strain of the virus is one of the most lethal, with mortality rates that can exceed 90% in untreated cases. EVD is characterised by sudden onset of fever, intense weakness, muscle pain, headache, and sore throat. This is followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash, impaired kidney and liver function, and in some cases, internal and external bleeding.
Transmission and Preventive Measures
The transmission of Ebola occurs through direct contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person. This includes blood, vomit, faeces, and other secretions. The health ministry has emphasised the importance of adhering to preventive measures, particularly in high-risk areas. These measures include:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water or using hand sanitiser.
- Practising social distancing to reduce the risk of virus spread.
- Avoiding contact with individuals exhibiting symptoms of the virus.
- Using personal protective equipment (PPE) when caring for infected patients.
Health Response and Community Involvement
The World Health Organization (WHO) is actively involved in the response efforts to contain the outbreak. They have deployed teams to work alongside local health authorities to trace contacts of confirmed cases and provide necessary medical care. WHO officials have stated that as case numbers are likely to increase, they are mobilising resources to ensure rapid response and protection for communities.
Historical Context of Ebola in the DRC
This outbreak marks the 16th documented occurrence of Ebola in the DRC since the virus was first identified in 1976 near the Ebola River. The last outbreak in 2020 resulted in six deaths, whereas the 2019 outbreak was particularly devastating, claiming over 2,000 lives. The persistent recurrence of Ebola outbreaks in the DRC highlights the challenges faced by the country, including ongoing conflict, limited healthcare resources, and public health challenges.
International and National Implications
The implications of this outbreak extend beyond the immediate health crisis. The DRC's vulnerability to Ebola is exacerbated by the socio-political landscape, which complicates response efforts. Ongoing conflicts in eastern provinces hinder access to healthcare and impede effective communication about preventive measures. Additionally, the international community closely monitors the situation, as outbreaks can have far-reaching consequences for regional and global public health.
Looking Ahead: What Happens Next?
As the outbreak continues, health officials will focus on containment measures and community education. The response teams will work diligently to identify and treat infected individuals while educating the public on preventive practices. There is a pressing need for increased funding and resources to bolster the healthcare infrastructure in the DRC, which has historically struggled to cope with health crises.
The emergence of new cases in the coming weeks will be crucial in determining the course of this outbreak. Continuous surveillance, contact tracing, and vaccination campaigns will be pivotal in controlling the spread of the virus and protecting vulnerable populations. The DRC's ability to manage this crisis will depend significantly on local and international collaboration.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of Ebola virus disease?
The symptoms of Ebola virus disease include fever, severe headache, muscle pain, weakness, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhoea, rash, and in some cases, bleeding. Symptoms typically appear 2 to 21 days after exposure to the virus.
How is Ebola transmitted?
Ebola is transmitted through direct contact with the bodily fluids of an infected person, including blood, saliva, sweat, vomit, faeces, and semen. It can also be spread through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces.
What preventive measures can be taken to avoid Ebola infection?
Preventive measures include frequent handwashing, using personal protective equipment when caring for infected individuals, avoiding contact with sick persons, and practising social distancing in high-risk areas.
What is the mortality rate of the Zaire strain of Ebola?
The Zaire strain of Ebola has a high mortality rate, often exceeding 90% without treatment. Early medical intervention can significantly improve survival rates.
What should be done if someone is suspected to have Ebola?
If someone is suspected of having Ebola, they should be immediately isolated from others, and healthcare professionals should be notified. Testing and medical care should be sought as soon as possible.
As the situation develops, it is crucial to stay informed about Ebola outbreaks and the necessary precautions to take. The ongoing response efforts will play a significant role in controlling the spread of this deadly virus. #EbolaOutbreak #PublicHealth #DRCrisis



